What Does PMO Mean? A Comprehensive Guide on PMO Definition
If you’ve ever wondered about the driving force behind successful project execution in an organization, look no further than the PMO or Project Management Office. When you delve into the world of project management, you’ll likely encounter the term PMO. You might be wondering, “What does PMO mean?” The PMO is the backbone that provides oversight, support, and governance for project management operations.
Well, the PMO’s work and benefits aren’t confined here. If you want to know more about the most exciting acronym in project management, then this guide can help you. Read the article throughout its conclusion and explore PMO’s meaning, benefits, challenges, and significance. So, let’s get started!!
What is a PMO?

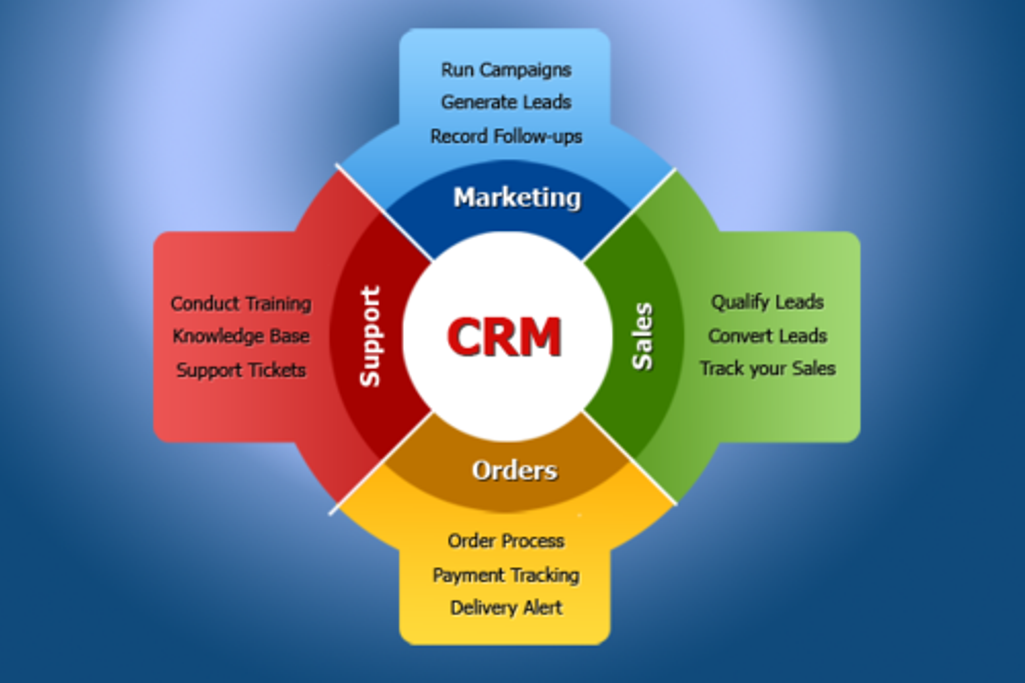
PMO stands for Project Management Office. It’s a department within an organization that provides oversight, ensures standards are met, and holds project teams accountable. The PMO’s primary focus is to ensure that projects are completed efficiently and effectively. It optimizes the entire project portfolio, maximizing the use of the organization’s resources.
In this case, the PMO acts almost like a steering committee, influencing decision-making and setting the direction for the projects within the organization. Its primary function is overseeing projects across an organization, ensuring they align with company standards. The PMO also holds teams accountable, which extends to project timeframes, resources, deliverables, and costs.
PMO Roles and Responsibilities
PMO roles and responsibilities extend to consolidating project tools. They are the curators, choosing and assembling a collection of templates, software, and work management tools to create a robust database. This repository is a goldmine, fostering data-driven decisions that augment the success of your projects.
- It underscores how the right blend of people, tools, and procedures can harmonize project management.
- One paramount role of the PMO is choosing the correct blend of projects that align with your organization’s larger vision and goals.
- Efficient implementation and management of the project is also a responsibility of PMO.
- Another critical function of the PMO is its commitment to continuously updating employees.
- Pooling resources effectively is another core competence of the PMO.
- They’ll train and coach employees in standard procedures and methodologies, ensuring a harmonized approach to project management across the organization.
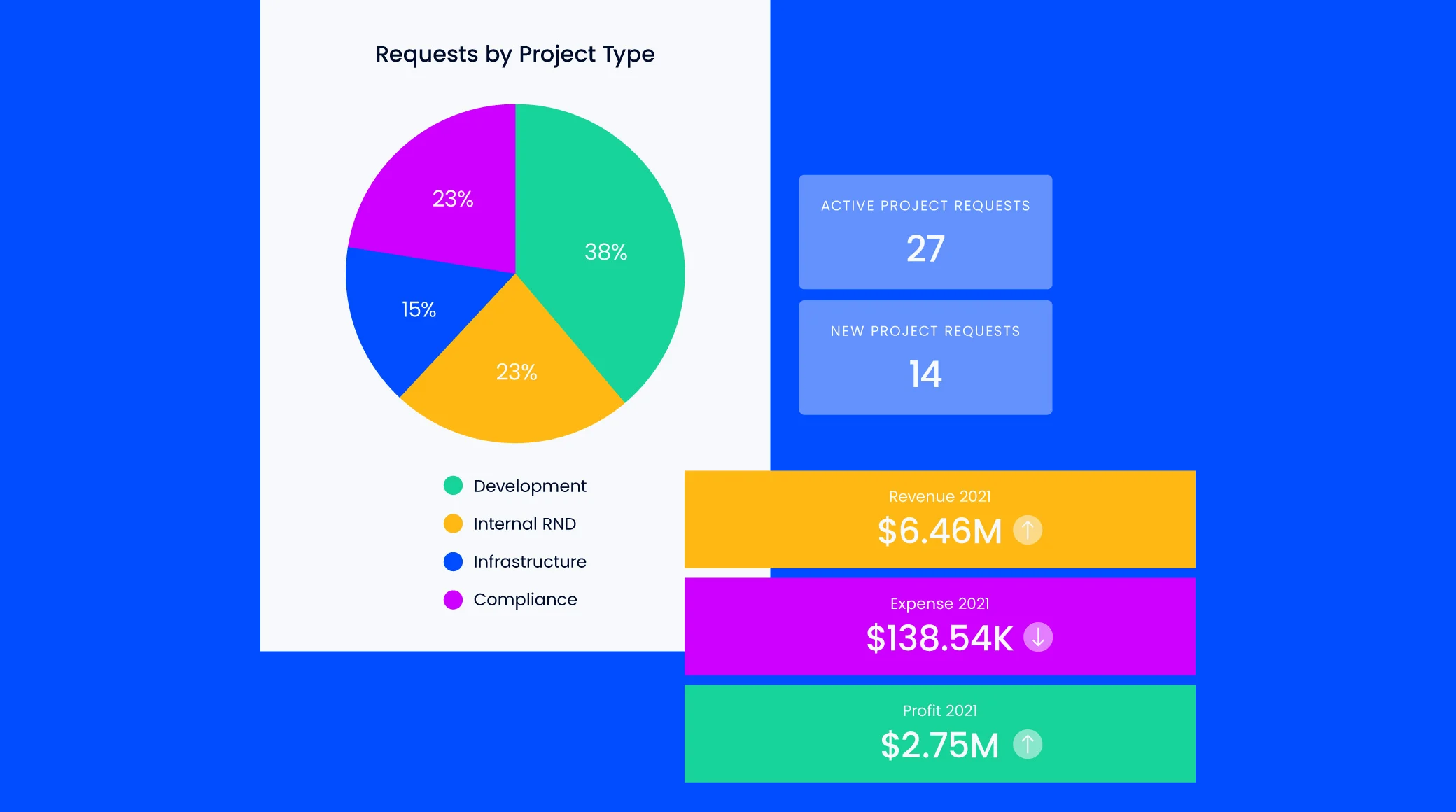
- The PMO is responsible for outlining project metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to keep track of project progress and success.
What are The Benefits of a PMO?

When you continuously ask yourself, “What does PMO mean in project management?” it’s time to delve into its tremendous potential benefits. A PMO is not just an acronym but a significant entity that can transform project management practices within your organization.
1. Standardized Processes
One of the significant benefits of a PMO is the standardization of processes. With a PMO, you’ll eliminate ambiguity in your project management practice and have clearly defined workflows. This is crucial if you’re aiming for efficiency in your operations. A standardized process eliminates gaps, reduces redundancy, and ultimately increases your organization’s productivity.
2. Enhanced Coordination
If you regularly find your team of specialist coders and developers spending too much time on project management, you might need a PMO. When a PMO acts as a coordinator or supervisor, your specialists can focus on what they do best. As a result, you’ll likely see a decrease in project duration and an increase in quality output.
3. Tangible Benefits
The success of a project is often measured by its tangible benefits. You will likely attain better project results with a PMO in place and managing project scopes efficiently. You’ll quickly meet your timelines and budgets, directly translating into consumer benefits.
4. Tool Consolidation
One of the unsung PMO roles is the consolidation of project tools to create a robust database. Using modern project management tools can lend a significant productivity boost. Having all your project data in one place facilitates data-driven decision making, giving your projects the best probability for success..
Different Types of Project Management Office

When considering what PMO means in project management, it’s crucial to note that different PMOs exist tailored to varied organizational needs. By assessing these types and their distinct functions, you’ll discern the best fit for your project management challenges and goals.
1. Program Management Office (PgMO)
As a program management office, the primary function of a PgMO is not to oversee individual projects but rather to support the success of programs. These offices play a crucial role in developing and managing business strategies. In specific scenarios, project management offices (PMOs) may report to them, given that managing multiple projects often culminates in the formation of a program.
2. Portfolio Management Office (PPMO)
Where multiple projects and programs form a portfolio, a Project Portfolio Management Office (PPMO) steps in. The PPMO’s duty revolves around overseeing these portfolios. Additionally, PPMOs facilitate crucial insights into the state of operations for stakeholders and managers—they stand as the executive decision-makers in this setting.
3. Project Support Office (PSO)
A Project Support Office differs from a PMO in its supportive, rather than managerial, role. A key function of PSOs is organizing and planning multiple projects to ensure their seamless operation.
4. Project Controls Office (PCO)
As a Project Controls Office, the principal role involves overseeing control systems related to costs and scheduling associated with project management. The central focus is on the speed, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of projects under its purview.
5. Delivery Management Office (DMO)
Stepping in to fine-tune the delivery aspect of project management, a Delivery Management Office shoulders the responsibility of ensuring that project processes flow and ultimately reach the finish line, delivering value to stakeholders.
6. Change Management Office (CMO)
Projects invariably trigger change, and a Change Management Office is designed to manage this aspect. The responsibilities include overseeing change management plans and ensuring smooth project transformation processes.
7. Product Management Office (PrMO)
Finally, the Product Management Office oversees processes from the conception to the delivery of products. They drive product strategy and roadmapping and work with other teams to ensure that the output meets organizational goals and customer requirements. Implementing a PrMO can lead to improved product success rate, customer satisfaction, and increased return on investment.
Essential Software Features to Establish a PMO
In your journey to understand “what does PMO mean in project management“, it’s crucial to become familiar with the vital features that streamline your PMO. These technologically enabled tools form the backbone of effective project management in a digitally driven world.
1. Software Project Documentation
Having organized, accessible Software project documentation is key. It’s an essential feature that can help manage all of your project’s documents and assets in one easy-to-access place. Assign owners, continually update statuses, use it to keep track of files, everything is streamlined. Encouraging your teammates to update their documents and statuses, it’s possible to keep everyone aligned effectively.
2. High-Level Project Plans
Before you can even consider embarking on any project goals or activities, you’ll need well-thought-out High-level project plans. Their formats often vary, depending on each project’s unique methodology and workflow. Organizing them comprehensively tidily is a crucial step in the right direction.
3. Project Roadmap
A detailed project roadmap is crucial to the entire PMO process. This tool helps teams concentrate on the project’s broader goals. With all the minutiae involved in any project, it’s easy to lose sight of the big picture – a robust and adaptable roadmap keeps you on course. This roadmap isn’t static; change is constant due to varying markets, customer needs, and shifting organizational goals.
4. Resource Management
Resource management is one of those features you can’t do without a PMO. It is paramount to oversee the allocation and utilization of your organizational resources promptly and optimally. The more accurate your resource management, the higher your productivity will become.
5. Feature or Product Backlog
A Feature or product backlog is also an indispensable feature in any PMO. It’s a prioritized list of all the features or tasks that need to be done on a project, with the ones of highest importance at the top. Using this feature, you can manage your work efficiently, ensuring no task is overlooked or forgotten.
6. Real-Time KPI Reports and Dashboards
The need for Real-time KPI reports and dashboards can’t be overstated. These tools allow you to track, analyze, and report on your project’s performance. They also help you identify shortcomings in real time and make timely decisions.
What Are The Challenges of a PMO?
A Project Management Office (PMO) is not devoid of challenges with any organizational system. While PMOs aim to streamline operations and raise efficiency in project management, they come with their own set of difficulties. Their structured processes and procedures may at times be perceived as inflexible or burdensome by project managers and teams alike.
1. Adaptability Issue
Primarily, adaptability issues often surface. Transitioning to a PMO-led model from an unstructured environment can pose a challenge, especially if your organization is unaccustomed to consistent practices. Applying PMO standards calls for substantial change management efforts.
2. Resource Allocation
Another strain is resource allocation. Identifying the right personnel to staff your PMO – those who understand project management from a holistic perspective – can be a hurdle. Bearing in mind, the extent of your PMO’s authority influences whether you have the appropriate resources.
3. Project Methodologies
Yet another challenge is molding diverse project methodologies under one framework. What’s crucial here is to find a balance between allowing project managers the freedom to use methodologies they’re comfortable with and yet, adhering to PMO’s established processes.
4. Demand for Frequent and Clear Communication
There’s also a demand for frequent and clear communication. This becomes increasingly difficult with complex projects and broad teams and may contribute to execution issues. A PMO must, therefore focus on developing effective communication systems.
5. Significant Investment
Finally, establishing a PMO requires a significant investment of time, effort, and, potentially, capital. The organization would need to be convinced of a PMO’s long-term value despite the upfront costs.
Conclusion
In the above article, we have explored the complexities of establishing a PMO and understood the challenges that may arise, from adaptability issues to resource allocation. Moreover, it is essential to integrate diverse project methodologies and maintain clear communication. The road to PMO implementation may be tough, but it’s worth the effort.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the main challenges of establishing a PMO?
Establishing a PMO can present several challenges, including issues with adaptability when transitioning to a structured PMO model, difficulties in resource allocation for staffing, the challenge of integrating diverse project methodologies, maintaining clear communication, and a significant investment of time, effort, and capital.
Q2. How can organizations overcome the challenges of establishing a PMO?
Overcoming the challenges of establishing a PMO often requires a careful and considered strategy that includes effective resource allocation, seamless integration of project methodologies, clear and consistent communication, and a commitment to a substantial investment of time, resources, and capital.
Q3. Why is it critical to overcome these challenges to establish a PMO?
Overcoming these challenges is crucial for organizations to gain the benefits of improved communication, coordination, and project execution that come with the effective implementation of a PMO.
Q4. What are the potential benefits of establishing a PMO?
PMOs can provide numerous benefits, including improved communication, increased project visibility, better resource management, and increased project success rates. A proficiently run PMO can be instrumental in achieving strategic organizational goals.
Q5. How does a PMO contribute to communication improvement within an organization?
A PMO can improve communication by providing a unified platform for information sharing. It allows transparency and visibility across projects, facilitating better decision-making by keeping all stakeholders informed and aligned.